
The Application of Embedded Systems in the Medical Field
Global electronic component supplier AMPHEO PTY LTD: Rich inventory for one-stop shopping. Inquire easily, and receive fast, customized solutions and quotes.
Embedded systems play a crucial role in modern healthcare, enhancing medical diagnostics, treatment, patient monitoring, and hospital management. Their reliability, real-time processing, and low-power operation make them ideal for medical applications. Below are key areas where embedded systems are applied in the medical field.
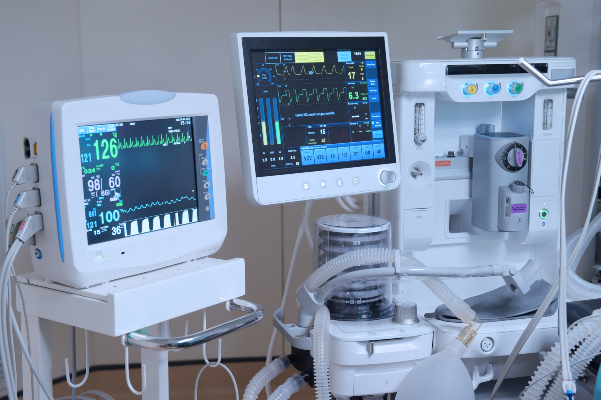
1. Medical Diagnostic Devices
Embedded systems are widely used in diagnostic equipment to improve accuracy and efficiency.
-
Digital Imaging Systems (MRI, CT Scans, Ultrasound, X-ray)
-
Embedded processors control image acquisition, processing, and display.
-
Real-time signal processing enhances image clarity for better diagnosis.
-
-
Blood Glucose Monitors
-
Microcontrollers analyze blood samples and display glucose levels instantly.
-
Some devices connect to smartphones for data tracking.
-
-
ECG (Electrocardiogram) Machines
-
Embedded systems process electrical signals from the heart to detect abnormalities.
-
Portable ECG monitors allow remote patient monitoring.
-
-
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Machines
-
Used in DNA analysis (e.g., COVID-19 testing).
-
Embedded controllers manage precise temperature cycles for DNA amplification.
-
2. Patient Monitoring Systems
Embedded systems enable continuous health tracking, reducing hospital stays and improving care.
-
Wearable Health Monitors (Smartwatches, Fitness Bands)
-
Track heart rate, SpO2, sleep patterns, and physical activity.
-
Use low-power microcontrollers (e.g., ARM Cortex-M) for long battery life.
-
-
ICU & Hospital Monitoring Systems
-
Embedded computers monitor vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels).
-
Alerts medical staff in case of emergencies.
-
-
Remote Patient Monitoring (Telemedicine)
-
IoT-enabled embedded devices transmit patient data to doctors in real time.
-
Reduces the need for frequent hospital visits.
-
3. Therapeutic and Surgical Devices
Embedded systems assist in treatment and surgical procedures for better precision.
-
Infusion Pumps
-
Deliver precise doses of medication (e.g., insulin pumps).
-
Safety-critical systems with fail-safe mechanisms.
-
-
Pacemakers & Implantable Defibrillators
-
Microcontrollers regulate heart rhythms in patients with arrhythmia.
-
Must be highly reliable with ultra-low power consumption.
-
-
Robotic Surgery Systems (e.g., da Vinci Surgical System)
-
Use real-time embedded controllers for precision movements.
-
Enhance minimally invasive surgeries.
-
-
Nerve & Muscle Stimulators
-
Help in rehabilitation (e.g., TENS machines for pain relief).
-
4. Medical Laboratory Automation
Embedded systems streamline lab processes for faster and more accurate results.
-
Automated Analyzers (Blood, Urine, Biochemistry Tests)
-
Robotic arms and sensors controlled by embedded systems handle samples.
-
Reduce human error and increase throughput.
-
-
PCR & DNA Sequencers
-
Embedded firmware manages thermal cycling and data analysis.
-
5. Hospital & Healthcare Management Systems
Embedded computing improves hospital operations and data management.
-
Smart Hospital Beds
-
Monitor patient movements to prevent bedsores.
-
Adjust positions automatically for comfort.
-
-
RFID & IoT-Based Asset Tracking
-
Track medical equipment, drugs, and patient records.
-
Reduces losses and improves efficiency.
-
-
Pharmacy Automation Systems
-
Robotic dispensers ensure accurate medication distribution.
-
Challenges in Medical Embedded Systems
-
Safety & Reliability – Must comply with strict regulations (e.g., FDA, ISO 13485).
-
Security – Protection against cyber threats (e.g., hacking of pacemakers).
-
Power Efficiency – Critical for implantable and portable devices.
-
Real-Time Processing – Delays in data processing can be life-threatening.
Future Trends
-
AI & Machine Learning in Diagnostics (e.g., AI-powered ECG analysis).
-
More Wearable & Implantable Devices (e.g., smart contact lenses for glucose monitoring).
-
5G & Edge Computing for faster telemedicine and remote surgeries.
-
Biodegradable Embedded Sensors for temporary medical implants.
Conclusion
Embedded systems are revolutionizing healthcare by enabling smarter diagnostics, real-time monitoring, and advanced treatments. As technology evolves, their role in medicine will continue to expand, improving patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Related Articles
- ·What are the advantages and disadvantages of using SoCs in embedded systems?
- ·How to implement a multi class neural network with STM32F103?
- ·The Difference Between 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, And 64-bit Microcontrollers
- ·The difference between HEX and BIN files in microcontrollers
- ·Application of Embedded Systems in Industrial Robots
- ·Application of Embedded Systems in Aerospace and Defense Fields
- ·The application of embedded systems in the field of automotive electronics
- ·Design and Implementation of a Smart Home System Based on STM32
- ·Implementing AI and machine learning on low-power MCUs
