
The application of embedded systems in the field of automotive electronics
Global electronic component supplier AMPHEO PTY LTD: Rich inventory for one-stop shopping. Inquire easily, and receive fast, customized solutions and quotes.
Embedded systems are critical to modern automotive electronics, enabling advanced functionality, safety, and efficiency. They are used in various subsystems, from engine control to infotainment. Below are key applications with real-world examples.
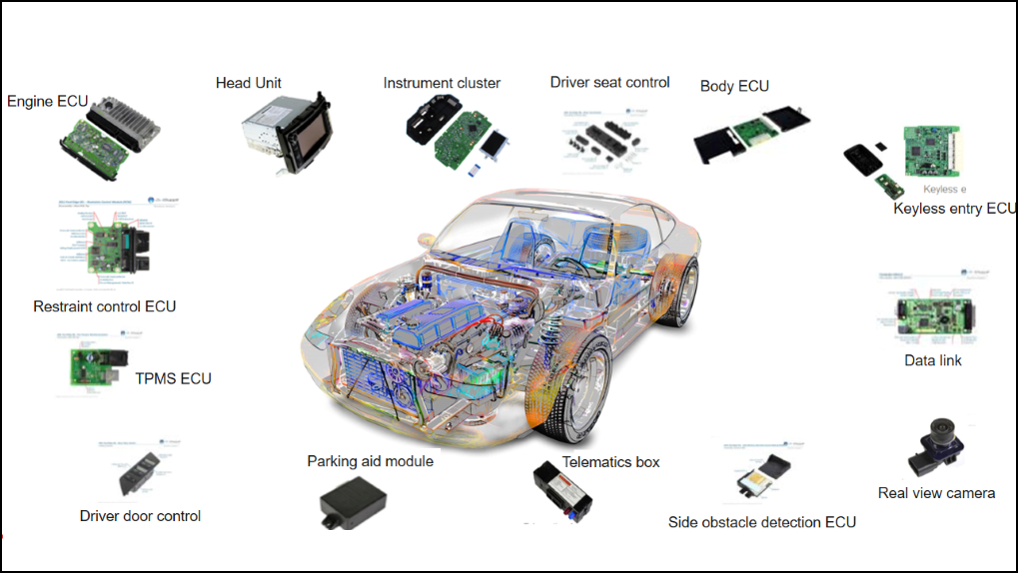
1. Engine Control & Powertrain Management
Function: Optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions.
Example:
-
ECU (Engine Control Unit) – Monitors sensors (oxygen, throttle position) and adjusts fuel-air mixture (e.g., Bosch Motronic ECU).
-
Hybrid/Electric Vehicle Control – Manages battery systems (e.g., Tesla’s Battery Management System).
2. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Function: Enhance safety via sensors and automated responses.
Examples:
-
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) – Uses radar (e.g., Tesla Autopilot, Mercedes-Benz Distronic).
-
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) – Detects collisions and applies brakes (e.g., Subaru EyeSight).
-
Lane-Keeping Assist (LKA) – Adjusts steering via cameras (e.g., Toyota Lane Tracing Assist).
3. Infotainment & Telematics
Function: Provide navigation, media, and connectivity.
Examples:
-
Tesla’s Touchscreen System – Runs on Linux-based embedded OS.
-
Android Automotive OS – Used in Volvo, Polestar for apps and voice control.
-
eCall Systems – Automatic emergency calls (e.g., EU-mandated in BMW, Audi).
4. Body Electronics & Comfort Systems
Function: Control lighting, climate, and security.
Examples:
-
Keyless Entry & Start – RFID-based (e.g., Nissan Intelligent Key).
-
Automatic Climate Control – Adjusts temperature via sensors (e.g., Toyota’s Smart Climate).
-
Matrix LED Headlights – Adjust beam patterns (e.g., Audi Matrix LED).
5. Vehicle Networking (CAN, LIN, Ethernet)
Function: Enable communication between ECUs.
Examples:
-
CAN Bus – Used for engine, transmission, and brake communication (e.g., OBD-II diagnostics).
-
Ethernet Backbone – High-speed data for ADAS (e.g., BMW’s use in iX).
6. Electric & Hybrid Vehicle Systems
Function: Manage battery, charging, and energy recovery.
Examples:
-
BMS (Battery Management System) – Monitors cell voltage (e.g., Tesla’s 4680 battery pack).
-
Regenerative Braking – Converts kinetic energy to electricity (e.g., Toyota Prius).
7. Autonomous Driving (L2-L4)
Function: Process sensor data for self-driving.
Examples:
-
NVIDIA DRIVE Platform – Runs AI algorithms for perception (e.g., Mercedes-Benz DRIVE PILOT).
-
Mobileye EyeQ Chips – Power camera-based ADAS (e.g., Ford BlueCruise).
Why Embedded Systems Dominate Automotive Electronics?
✔ Real-time processing – Critical for safety (e.g., airbag deployment in milliseconds).
✔ Low power consumption – Essential for electric vehicles.
✔ Modularity – Allows incremental upgrades (OTA updates in Tesla).
With trends like connected cars, V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything), and AI-driven autonomy, embedded systems will remain the backbone of automotive innovation.
Here are real-world examples of embedded systems in automotive electronics, categorized by key applications with technical details and industry implementations:
1. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Example: Tesla Autopilot (Hardware 3.0)
-
Embedded Tech:
-
SoC: Custom Tesla-designed FSD (Full Self-Driving) chip (14nm, dual-core AI accelerator).
-
Sensors: 8 cameras, 12 ultrasonic sensors, forward radar.
-
Software: Neural networks for object detection (e.g., "HydraNet" multi-task learning).
-
-
Function: Lane centering, automatic lane changes, traffic-aware cruise control.
-
Why Embedded?: Real-time processing (<100ms latency) with low power consumption (72W TDP).
Example: Mobileye EyeQ5 (Used by BMW, Ford)
-
Embedded Tech:
-
SoC: EyeQ5 (7nm, 12-core CPU + GPU + dedicated accelerator cores).
-
Function: Powers L2+/L3 systems like Ford BlueCruise (hands-free highway driving).
-
2. Electric Vehicle Powertrain
Example: Tesla Model 3 Battery Management System (BMS)
-
Embedded Tech:
-
MCU: Texas Instruments Hercules TMS570 (ASIL-D certified for safety).
-
Function: Monitors 2,976 battery cells (in Long Range pack), balances charge/discharge, predicts range.
-
Innovation: Uses machine learning to optimize battery degradation over time.
-
Example: Nissan Leaf Motor Controller
-
Embedded Tech:
-
MCU: Renesas RH850 (32-bit, dual-core).
-
Function: Converts DC battery power to AC for the motor, manages regenerative braking.
-
3. Infotainment & Telematics
Example: Volvo Cars with Android Automotive OS
-
Embedded Tech:
-
SoC: Qualcomm Snapdragon 8155 (7nm, 8-core).
-
OS: Linux-based Android Automotive (not Android Auto!).
-
Features: Native Google apps (Maps, Assistant), OTA updates, voice control.
-
Example: Mercedes-Benz MBUX Hyperscreen
-
Embedded Tech:
-
SoC: NVIDIA Xavier (512-core Volta GPU + 8-core CPU).
-
AI: Learns driver habits (e.g., suggests frequent destinations).
-
4. Vehicle Networking
Example: CAN Bus in Volkswagen Group Vehicles
-
Embedded Tech:
-
Protocol: CAN FD (Faster Data Rate variant of CAN).
-
Use Case: Connects >70 ECUs in a VW ID.4 (e.g., transmission talks to battery).
-
Challenge: Security risks (e.g., CAN injection attacks).
-
Example: Automotive Ethernet in BMW iX
-
Embedded Tech:
-
Protocol: 10Gbps Ethernet backbone (vs. CAN’s 1Mbps).
-
Use Case: Handles 4K camera feeds for autonomous driving.
-
5. Autonomous Driving (L4)
Example: Waymo Driver (Jaguar I-PACE Robotaxi)
-
Embedded Tech:
-
Compute: 5x custom Google TPU pods (for perception).
-
Sensors: LiDAR + 360° cameras + radar.
-
Key Feature: Runs without safety driver (L4 in Phoenix, AZ).
-
Example: NVIDIA DRIVE Orin in NIO ET7
-
Embedded Tech:
-
SoC: Orin (254 TOPS AI performance).
-
Function: Powers NIO’s "NAD" (Autonomous Driving) with 4D imaging radar.
-
6. Cybersecurity
Example: Tesla’s Intrusion Detection System
-
Embedded Tech:
-
Hardware: Hardware security module (HSM) in FSD computer.
-
Software: Signed firmware updates + CAN bus encryption.
-
Recent Hack: Researchers breached Tesla via Bluetooth (patched via OTA).
-
7. Classic vs. Modern: Evolution of Embedded in Cars
| System | 1990s (Example) | 2020s (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Control | 8-bit ECU (Bosch Motronic) | 32-bit MCU (AURIX TC3xx, ASIL-D) |
| Infotainment | CD Player (Mazda Miata) | 5G-connected Android OS (Polestar 3) |
| Safety | Airbag (single sensor) | Multi-sensor ADAS (Tesla Vision) |
Why These Examples Matter?
-
Performance: Embedded systems enable real-time response (e.g., AEB must act in <50ms).
-
Scalability: Same ECU hardware can be reprogrammed via OTA (e.g., Tesla adding features post-purchase).
-
Safety: ASIL-D certified MCUs (e.g., in brakes) reduce failure rates to <1 per billion hours.
Related Articles
- ·The best MCUs/MPUs for industrial humanoid robots
- ·What are the advantages and disadvantages of using SoCs in embedded systems?
- ·Comparison of ARM vs. RISC-V MCUs
- ·SoC vs SoM: What's the Difference?
- ·Digital Signal Processors vs x86 Architecture, What's the Different?
- ·How to determine the performance limit of a microcontroller?
- ·The Application of Embedded Electronics in the Field of Consumer Electronics
- ·Application of Embedded Systems in Industrial Robots
- ·Application of Embedded Systems in Aerospace and Defense Fields
