
Examining Transformer Substitutes: Converting 220V to 110V
November 06 2023 
Inquiry
Global electronic component supplier AMPHEO PTY LTD: Rich inventory for one-stop shopping. Inquire easily, and receive fast, customized solutions and quotes.
QUICK RFQ
ADD TO RFQ LIST
Transformers are crucial parts of a lot of electrical systems. They facilitate the effective transmission and distribution of electricity by stepping up or stepping down voltage. Transformers may not always be available in the size or configuration that you require, and they can be costly and unwieldy. There might be transformer alternatives available in some circumstances that work just as well. In this blog, we will examine some transformer substitutes that can be used to convert 220V to 110V. We will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each option, and we will provide instructions on how to use them safely.
How Transformers Work?
Transformers function by using a magnetic field to move electrical energy from one circuit to another. They are made up of a common core encircled by two wire coils. While the secondary coil is connected to the load, the primary coil is connected to the source voltage. A magnetic field is produced in the core when the primary coil is subjected to an alternating current (AC). The secondary coil then experiences a voltage due to this magnetic field. The voltage applied to the primary coil and the total number of turns in each coil determine the voltage induced in the secondary coil.How to Test a Transformer with a Multimeter?
If the voltage readings are different, the transformer is faulty and needs to be replaced. Using a multimeter to test a transformer can help verify your suspicions if you think it may be defective. Use a multimeter to test a transformer by doing the following steps:- In the AC voltage mode, set the multimeter.
- Attach the multimeter's black lead to the transformer's ground terminal.
- Attach the multimeter's red lead to one of the transformer's other terminals.
- Obtain a voltage reading.
- For the transformer's other terminal, repeat steps 3 and 4.
How to Identify a Faulty Transformer?
Finding a malfunctioning transformer is essential to keeping your electrical system safe and functional. These are a few typical indicators of a failing transformer:- Overheating: Inadequate ventilation or excessive load can cause transformers to overheat. This may shorten the transformer's life and cause damage.
- Buzzing noises: A malfunctioning transformer may produce a buzzing noise. This is brought on by the core of the transformer vibrating.
- Voltage fluctuations: Your electrical system's voltage may fluctuate due to a malfunctioning transformer. Appliances and electronic devices may be harmed by this.
- Burning smell: A malfunctioning transformer is indicated if you detect a burning smell.
Understanding the Need for Transformer Substitutes
Transformer substitutes, also known as voltage converters, are devices that convert electrical power from one voltage level to another. When utilizing appliances or gadgets intended for a voltage different from the available power source, this is frequently required. For example, to use your 110V appliance safely when visiting a country with a 220V power grid, you will need to bring a transformer replacement.Common Transformer Substitutes
Autotransformers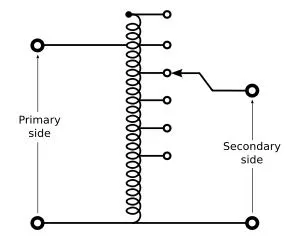


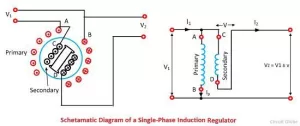
How do you convert 220v to 110v without a transformer?
Method 1: Using a Voltage Divider One easy way to lower voltage is to use a voltage divider circuit, which dissipates some of the power as heat. However this approach is ineffective, and it isn't appropriate for high-power appliances. To create a voltage divider, you will need two resistors with equal values. Assign the resistors a series connection across the input voltage of 220V. About 110V will be half of the input voltage which is the output voltage. Method 2: Using a Rectifier and Inverter With this method, a rectifier is used to convert the 220V AC input voltage to DC voltage, and an inverter is used to reverse the DC voltage and return it to AC voltage at 110V. But this approach is more involved and needs specific parts. It is crucial to remember that utilizing a transformer is a safer and more dependable option and that each of these approaches has drawbacks. Before attempting to convert 220V to 110V without a transformer, it is strongly advised that you consult with a qualified electrician if you are unfamiliar with electrical circuits.Advantages of Transformer Substitutes
- Cost: Compared to traditional transformers, transformer replacements are frequently more affordable. They might use less expensive materials or fewer components, which would cut the cost of production and upkeep.
- Size and Weight: Compared to original transformers, transformer replacements are frequently smaller and lighter. This can be helpful when there is a need to reduce weight or space, like in portable electronics or tiny electronic systems.
- Efficiency: When compared to conventional transformers, some transformer replacements, such as power converters or solid-state transformers, can provide higher efficiency. They can reduce power consumption and operating costs by minimizing energy losses and increasing overall system efficiency.
- Flexibility: Transformer alternatives may offer more flexibility in terms of converting and adjusting voltage. They might provide more options for voltage or allow you to change the output voltage as needed. This can be useful in situations where different voltage levels are needed, like adjustable power supplies or variable speed drives.
- Isolation: A few transformer alternatives, such as voltage regulators or flyback converters, can offer electrical isolation between the input and output. By preventing electrical shocks and lowering the possibility that connected devices will be damaged, this isolation can improve safety.
Disadvantages of Transformer Substitutes
- Limited Power Handling: The amount of power that certain transformer replacements can handle may be restricted. They might not be appropriate for high-power uses, or they might need extra parts to manage greater voltages or currents.
- Complexity: Compared to conventional transformers, some transformer alternatives, such as power converters and solid-state transformers, may have more intricate designs and methods of operation. Installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting may require specific knowledge or expertise due to this complexity.
- Higher Cost: Certain advanced substitutes, like solid-state transformers or specialized power converters, can be more expensive than traditional transformers, even though they can occasionally be more affordable than transformers. The project budget as a whole may be impacted by a larger initial investment cost.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can be produced by certain transformer replacements, especially those that operate at high frequencies or with switching components. Further steps to reduce EMI are necessary because this interference may impair the functionality of adjacent electronic systems or devices.
- Compatibility Issues: Not all current systems or equipment are compatible with transformer substitutes. For correct integration and operation, they might need to be adjusted or modified. Compatibility problems can increase the overall system's design and implementation's complexity and expense.
Safety Precautions When Using Transformer Substitutes
When using transformer substitutes, it is important to follow safety precautions:- Never Exceed the Transformer Substitute's Power Output Rating: Don't go over the transformer substitute's power output rating. Overloading may result in the appliance you're using or the transformer substitute overheating and breaking.
- Use a Grounded Outlet: When using a transformer substitute, make sure you always use a grounded outlet. You'll be less vulnerable to electrical shock thanks to this.
- Keep the Transformer Substitute Cool: Avoid putting it in a small space or blocking any of its vents. Overheating may cause harm to the transformer replacement.
- Disconnect When Not in Use: Turn off the power supply to the transformer substitute by disconnecting it. This will lessen the chance of damage or accidental use.
Conclusion
Transformers enable voltage conversion and provide power to a variety of devices, making them essential parts of electrical systems. We have discussed many facets of transformers in this blog. Gaining a deeper comprehension of transformers will help you to address typical problems and make wise decisions about how to use them.FAQa about Transformer
How Much Does It Cost to Replace a Transformer? A transformer's replacement cost can vary based on several factors, including the type of transformer, its power rating, and the installation's complexity. You can buy small transformers for less than $10, which are used in doorbell circuits. On the other hand, large transformers—like the ones found in power substations—can get very expensive. How Long Does It Take to Fix a Transformer? The degree of damage and the availability of replacement parts can affect how long it takes to fix a transformer. While more involved repairs might take days or even weeks to complete, minor repairs can typically be finished in a few hours. How to Wire a Doorbell Transformer?- Cut the power supply: Make sure the main electrical panel has the power to the doorbell system off before you start.
- Locate and take out the outdated transformer: Find the doorbell transformer that is currently in place; it is usually installed in a junction box or on a wall. After removing the old transformer, disconnect the wires from the transformer's terminals.
- Install and link the replacement transformer: Put the new transformer in the same spot where the old one was secured. The new transformer's terminals should be connected to the following wires from your home's electrical system: black to black (hot), white to white (neutral), and green or bare wire to green (ground).
- Link the doorbell button wires: Join the doorbell button's wires to the appropriate transformer terminals.
- Safe wire connections: To insulate and safeguard the wire connections, use electrical tape.
- Activate the power, then check: Activate the power source located at the primary electrical panel. Press the doorbell button to see if everything is working as it should.
- Ask for help if you need it: Seek advice from a qualified electrician if you run into any problems or questions.
How Transformers WorkHow to Test a Transformer with a MultimeterHow to Identify a Faulty TransformerUnderstanding the Need for Transformer SubstitutesCommon Transformer SubstitutesHow to convert 220v to 110v without transformerAdvantages of Transformer SubstitutesDisadvantages of Transformer SubstitutesSafety Precautions When Using Transformer SubstitutesConclusionFAQa about TransformerHow Much Does It Cost to Replace a TransformerHow Long Does It Take to Fix a TransformerHow to Wire a Doorbell Transformer
Related Articles
- ·Stratix 10 VS Stratix V: Which FPGA is Right for Your Next Project?
- ·Intel Xeon Platinum 8454H vs AMD EPYC: Which Reigns Supreme?
- ·A Deep Dive into the AMD EPYC 4564P Processor
- ·MSP430F5438A vs MSP430F5529: A Detailed Analysis of Their Capabilities
- ·Comparing MSP430F6659 and MSP430F5419A: Which One is Right for Your Project?
- ·Exploring the Features of MSP430F5529 and MSP430F5638 Microcontrollers
- ·Demystifying 20 Microcontroller Projects for Beginners
- ·Unveiling the Ultimate Guide to Microcontroller Programming
- ·4680 Battery: Unveiling the Power Potential of the Next-Gen Cell
- ·Exploring the Case Studies on Arduino Applications
Populer Posts
