
Zener diode Symbol: A Comprehensive Overview
October 18 2023 
Inquiry
Global electronic component supplier AMPHEO PTY LTD: Rich inventory for one-stop shopping. Inquire easily, and receive fast, customized solutions and quotes.
QUICK RFQ
ADD TO RFQ LIST
The Zener diode is a fundamental component in electronics, known for its unique symbol and versatile applications. In this blog, we will delve into the world of Zener diodes, focusing on their symbol, functionality, and various applications. We will cover everything, including how to comprehend the Zener diode's function as well as its characteristics and testing procedures. In order to better comprehend the Zener diode symbol's meaning in electronic circuits, let's set out on a quest to solve its riddles.
What is a Zener diode Symbol?
The Zener diode symbol is a graphical representation of the Zener diode in circuit diagrams. Upon reaching a specific value, referred to as the zener voltage, a Zener diode, a particular type of semiconductor diode, can conduct current in either way. The ability of zener diodes to maintain a constant voltage output despite varying input voltage makes them a popular choice for voltage regulators. A triangle or arrowhead pointing in the direction of the cathode side of the diode is used as the Zener diode symbol, and two perpendicular lines, one extending upward and the other downward, are used as the cathode end.
Zener diode Characteristics
- Voltage Regulation: Zener diodes' capacity to regulate voltage is one of their key features. Zener diodes are made to function in the reverse bias zone, in contrast to conventional diodes that conduct current forward. The Zener voltage, often referred to as the breakdown voltage, is the point at which a Zener diode begins to conduct in the reverse direction, allowing a limited amount of current to flow. Zener diodes are perfect for voltage regulation applications due to their distinctive nature.
- Breakdown Voltage: A key factor in determining the Zener diode's capacity to regulate voltage is the breakdown voltage. It stands for the voltage at which the reverse-conducting of the Zener diode begins. The breakdown voltage ratings of zener diodes are predetermined and typically range from a few volts to several hundred volts. Engineers can accomplish perfect voltage regulation in their circuits by choosing a Zener diode with the proper breakdown voltage.
- Reverse Bias Operation: Zener diodes are made to work in the reverse bias area, which means that the cathode and anode of the device are linked to the power supply's positive and negative terminals, respectively. In this design, the Zener diode doesn't become conductive until the breakdown voltage is reached across it. The Zener diode begins to conduct when the breakdown voltage is reached, allowing current to flow in the opposite direction.
- Zener Impedance: Another crucial feature of Zener diodes is Zener impedance, also referred to as dynamic impedance. For a specific change in current, it shows the change in voltage across the diode. Since zeners typically have low impedance, even slight changes in current only cause minor changes in voltage. Because of this characteristic, Zener diodes are extremely steady and dependable for voltage regulation applications.
Video related to Zener diode Symbol
What is the purpose of a Zener diode?
A Zener diode is primarily used to control voltage in electrical circuits. When a precise value, called the Zener voltage, is attained, semiconductor devices called zener diodes are designed specifically to conduct current in the opposite direction. They are perfect for use in voltage regulation circuits because of this characteristic. Even if the input voltage changes, a parallel connection between a Zener diode and a load will keep the voltage across the load constant. In order to shunt any excess voltage away from the load, the Zener diode will conduct current in the opposite direction.Can a Zener diode be used as a voltage regulator?
Yes, a Zener diode can function as a voltage regulator. Voltage control is in reality one of a Zener diode's main functions. The Zener breakdown is a feature that a Zener diode displays when operating in the reverse bias region. At this time, the diode begins to conduct in the opposite way and permits a controlled quantity of electricity to pass. The precise value at which this happens is the breakdown voltage, also referred to as the Zener voltage. Engineers can use a Zener diode as a voltage regulator to keep the output voltage constant independent of changes in the input voltage by choosing one with the desired breakdown voltage. The Zener diode begins to conduct when the input voltage rises over the Zener voltage, efficiently shunting any excess current to the ground and maintaining the output voltage at the appropriate level. To use a Zener diode as a voltage regulator, it is typically connected in parallel with the load or in series with a current-limiting resistor. This configuration ensures that the Zener diode maintains a constant voltage across the load, even if the input voltage fluctuates. While Zener diodes can provide voltage regulation, it's crucial to remember that they are often employed in low-power applications. Zener diodes can be combined with other parts, like transistors or integrated circuits, to make voltage regulation circuits that are more reliable for increased power needs.How Does a Zener diode Work?
Zener breakdown is the underlying theory behind how Zener diodes operate. When a strong reverse voltage is supplied to a Zener diode, a phenomenon known as Zener breakdown takes place. The depletion region's electric field at this point is so powerful that it collapses, enabling current to flow in the opposite direction. The voltage at which zener breakdown takes place is known as the zener voltage. It is a distinctive quality of the Zener diode and is influenced by the junction width and doping concentration. Once Zener breakdown takes place, the Zener diode keeps a constant voltage between its terminals even when the current changes. Zener diodes are perfect for applications requiring voltage regulation due to this characteristic.Different Zener diode symbols
There are three different ways to draw a Zener diode symbol in schematics:- Standard Zener diode symbol
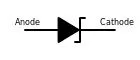
- Anode-cathode Zener diode symbol
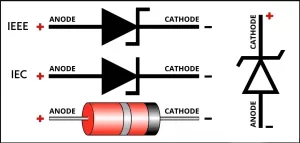
- Zener diode symbol with Zener voltage
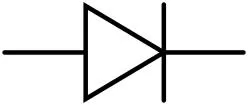
Zener diode vs. Schottky Diode
Schottky diodes are designed to have a very low forward voltage drop. This property makes them ideal for high-frequency applications and applications where low power loss is important. Here is a table that compares Zener diodes and Schottky diodes:| Characteristic | Zener diode | Schottky diode |
| Forward voltage drop | 0.7 V | 0.2-0.4 V |
| Reverse voltage drop | Zener voltage | Breakdown voltage |
| Reverse conduction | Yes, at Zener voltage | No |
| Switching speed | Slow | Fast |
| Applications | Voltage regulation, clipping and clamping | High-frequency applications, low power loss applications |
How does a Zener diode fall?
A Zener diode fails when the reverse voltage across the junction is raised above the zener voltage. Due to this, current flows backward through the Zener diode.Testing a Zener diode
There are a few different methods and techniques that can be used to test Zener diodes for proper functionality. Some of the most common methods include:- Forward bias testing: The Zener diode is connected in forward bias using this technique, and the forward voltage drop is then measured. The forward voltage drop of a Zener diode that is operating properly will be about 0.7 volts.
- Reverse bias testing: The Zener diode is connected in reverse bias for this type of testing, and the reverse leakage current is measured. Reverse leakage current will be extremely low in a Zener diode that is operating properly.
- Breakdown voltage measurement: This technique involves connecting the Zener diode in reverse bias and progressively raising the voltage until Zener breakdown takes place. After that, a voltmeter can be used to measure the Zener voltage.
What is a Zener diode used as?
- Surge protection: Zener diodes can be used to shield electronic circuits against surges and voltage spikes. The Zener diode conducts current to shunt any excess voltage away from the circuit when there is a rapid rise in voltage.
- Signal clamping: Zener diodes can be used to limit the voltage of signals. This is important for preventing signals from exceeding a specific voltage level, which might harm electrical components.
- Reference voltage generation: Zener diodes can be used to do this. The operating point of other components can be set using this reference voltage, which can also be used to compare other voltages.
- Power supplies: To ensure that electronic devices receive a constant voltage, zener diodes are employed to regulate voltage in power supplies.
- Electronic devices: Zener diodes are used for voltage control, surge protection, and other functions in various electronic devices, including computers, televisions, and smartphones.
- Automotive electronics: For voltage regulation and other uses, zener diodes are employed in-car electronics, including anti-lock braking and airbag systems.
- Industrial electronics: Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation, surge protection, and other functions in a variety of industrial electronic applications, including motor control systems and factory automation systems.
Conclusion
Zener diodes are essential electronics parts renowned for their distinctive symbol and wide range of uses. Among the many uses for them are voltage regulation, surge protection, signal clamping, and the creation of reference voltages. Zener diodes are perfect for a range of electronic projects since they are affordable and simple to utilize. You may utilize Zener diodes to design and construct dependable and effective electrical circuits if you have a solid understanding of how they operate and their numerous applications. What is a Zener diode SymbolZener diode CharacteristicsVideo related to Zener diode SymbolWhat is the purpose of a Zener diodeCan a Zener diode be used as a voltage regulatorHow Does a Zener diode WorkDifferent Zener diode symbolsZener diode vs. Schottky DiodeHow does a Zener diode fallTesting a Zener diodeWhat is a Zener diode used asConclusion
Related Articles
- ·Stratix 10 VS Stratix V: Which FPGA is Right for Your Next Project?
- ·Intel Xeon Platinum 8454H vs AMD EPYC: Which Reigns Supreme?
- ·A Deep Dive into the AMD EPYC 4564P Processor
- ·MSP430F5438A vs MSP430F5529: A Detailed Analysis of Their Capabilities
- ·Comparing MSP430F6659 and MSP430F5419A: Which One is Right for Your Project?
- ·Exploring the Features of MSP430F5529 and MSP430F5638 Microcontrollers
- ·Demystifying 20 Microcontroller Projects for Beginners
- ·Unveiling the Ultimate Guide to Microcontroller Programming
- ·4680 Battery: Unveiling the Power Potential of the Next-Gen Cell
- ·Exploring the Case Studies on Arduino Applications
Populer Posts
